
A good, but rather dry, introduction to setting up devices on a network can be found here.
#QLAB OSC GO MAC#
The sending device must be on the same network, and both the Mac running QLab and the other device must be configured correctly to share network traffic.

QLab accepts incoming OSC messages via TCP and UDP over a local network.
#QLAB OSC GO SOFTWARE#
You can use programs like Max/MSP, Medialon Manager, and TouchOSC, or hardware like ETC’s EOS family to send messages that exist in QLab 4’s OSC dictionary.Īlternately, if your software or hardware does not allow you to program your own messages, you can use the OSC controls in Workspace Settings to capture your device’s OSC messages, and map them to several of QLab’s workspace-level commands like GO, Panic, Load, and so on. Understanding OSCĪll software or devices which support OSC have their own dictionary of commands. OSC is a great way to control QLab from other software and hardware because it’s relatively simple to set up, requires no specialized hardware, and uses networking infrastructure that is often already in place, or easy to implement if not.
#QLAB OSC GO INSTALL#
You’ll need to install a license in order to use this cue.QLab has extensive support for the Open Sound Control protocol, a network communication standard for computers and multimedia devices. A license is required to reactivate this saved cue. This is only relevant for OSC cues set to the Raw UDP string type. No UDP message specified.įill in a valid UDP string in the Settings tab of the inspector. This is only relevant for OSC cues set to the Custom OSC message type. Invalid OSC message.įill in a valid OSC message in the Settings tab of the inspector. No OSC message specified.įill in a valid OSC message in the Settings tab of the inspector. This is only relevant for OSC cues set to the QLab OSC message type. Invalid command parameters.įill in valid parameters in the Settings tab of the inspector.
Missing QLab cue number.įill in a valid cue number in the Settings tab of the inspector. You may also need to visit the OSC section of Settings and specify a valid destination address and port for the desired patch. OSC cues can become broken for the following reasons: Invalid network destination.Īssign a valid network destination in the Settings tab of the inspector. Click this button to test-send your message. Some software, such as Medialon Manager, can accept commands as plaintext strings over UDP, and while this isn’t technically OSC, we use the OSC cue as the place to achieve this. This option allows you to send strings over UDP which will not be encoded as OSC by QLab on the way out. That sends message message to address /my/groovy with three integers, 2, 10, and 12, as separate arguments. Multiple arguments in a custom OSC message are separated by spaces, like this: For example, to tell a remote copy of QLab to GO, enter the command /go. This option gives you a text field to enter any OSC command. Enter a cue number below, and choose a command to send to the remote copy of QLab. For convenience when using OSC cues to communicate with another computer running QLab, this option provides a very simple interface for sending several commonly used commands. Select which type of message you want to send.
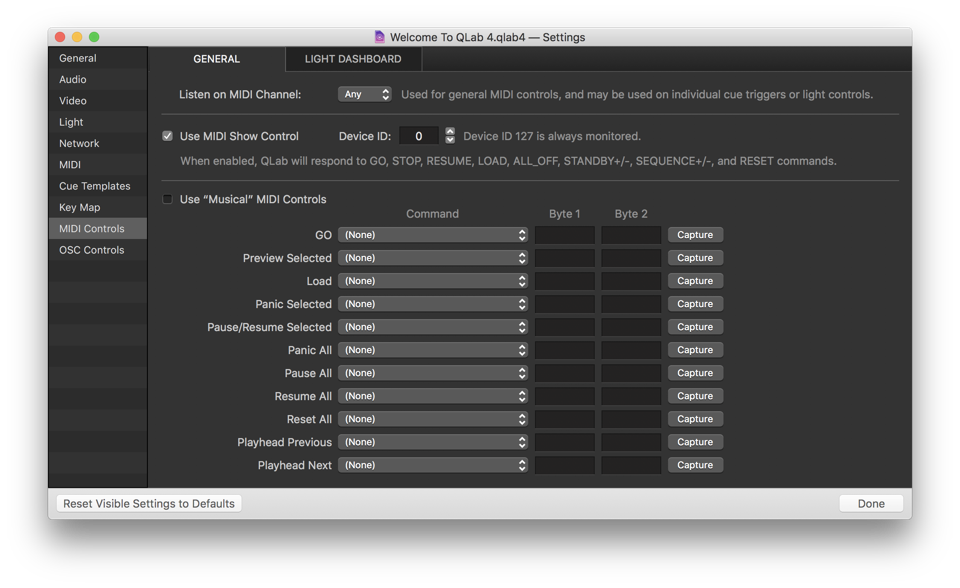
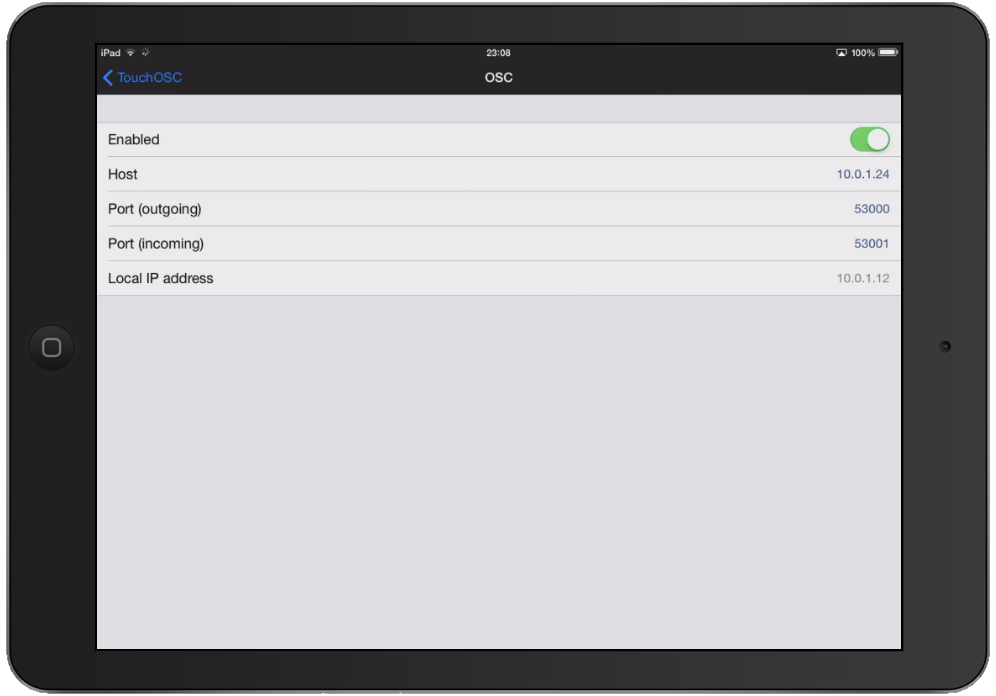
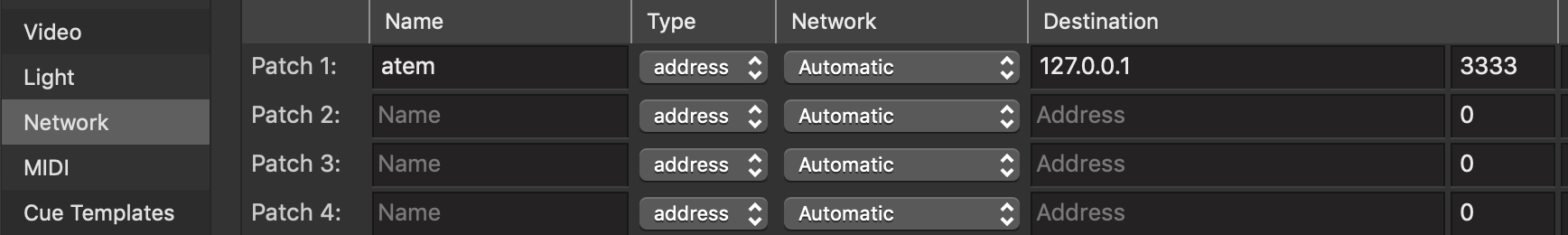
This drop-down menu shows the sixteen OSC patches, or destinations, to which QLab can send OSC messages. Please refer to the section on the inspector in the Getting Started section of this documentation. When an OSC cue is selected, two tabs will appear in the Inspector: OSC cues allow QLab to send messages using the Open Sound Control protocol a flexible, extensible, network-based messaging system designed as a sort of successor to MIDI.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
